2010 NY Slip Op 51482(U)
ARGENT MORTGAGE COMPANY, LLC, Plaintiff,
v.
DAPHINE MAITLAND, ET. AL., Defendants.
41383/07.
Supreme Court, Kings County.
Decided August 19, 2010.
Melissa A Sposato, Esq., Law Offices of Jordan Katz, PC, Melville NY, Plaintiff.
No Appearances, Defendant.
ARTHUR M. SCHACK, J.
In this mortgage foreclosure action, plaintiff’s motion for an order of reference for the premises located at 732 Hendrix Street, Brooklyn, New York (Block 4305, Lot 22, County of Kings) is denied with prejudice. The complaint is dismissed. The notice of pendency filed against the above-named real property is cancelled. Plaintiff’s successor in interest, AMERICAN HOME MORTGAGE SERVICING, INC. (AHMSI), lacks standing to continue this action because the instant mortgage was satisfied on April 26, 2010. Plaintiff’s counsel never notified the Court that the mortgage had been satisfied and failed to discontinue the instant action with prejudice. I discovered that the mortgage had been satisfied by personally searching the Automated City Register Information System (ACRIS) website of the Office of the City Register, New York City Department of Finance. AHMSI’s President and Chief Executive Officer or its Executive Vice President, Chief Legal Officer and Secretary Jordan D. Dorchuck, Esq., its counsel, Melissa A. Sposato, Esq. and her firm, Jordan S. Katz, P.C., will be given an opportunity to be heard as to why this Court should not sanction them for making a “frivolous motion,” pursuant to 22 NYCRR §130-1.1.
Background
Defendant DAPHINE MAITLAND (MAITLAND) borrowed $392,000.00 from original plaintiff ARGENT MORTGAGE COMPANY, LLC (ARGENT), on August 4, 2006. The loan was secured by a mortgage, recorded by ARGENT, at the Office of the City Register of the City of New York, New York City Department of Finance, on August 23, 2006, at City Register File Number (CRFN) XXXXXXXXXX. Defendant MAITLAND allegedly defaulted in her mortgage loan payments with her June 1, 2007 payment. ARGENT commenced the instant action with the filing of the summons, complaint and notice of pendency with the Kings County Clerk on November 8, 2007. Plaintiff’s counsel, on April 14, 2009, filed the instant motion for an order of reference with the Court’sForeclosure Department. After reviewing the papers, the Foreclosure Department forwarded the instant motion to me on August 16, 2010.
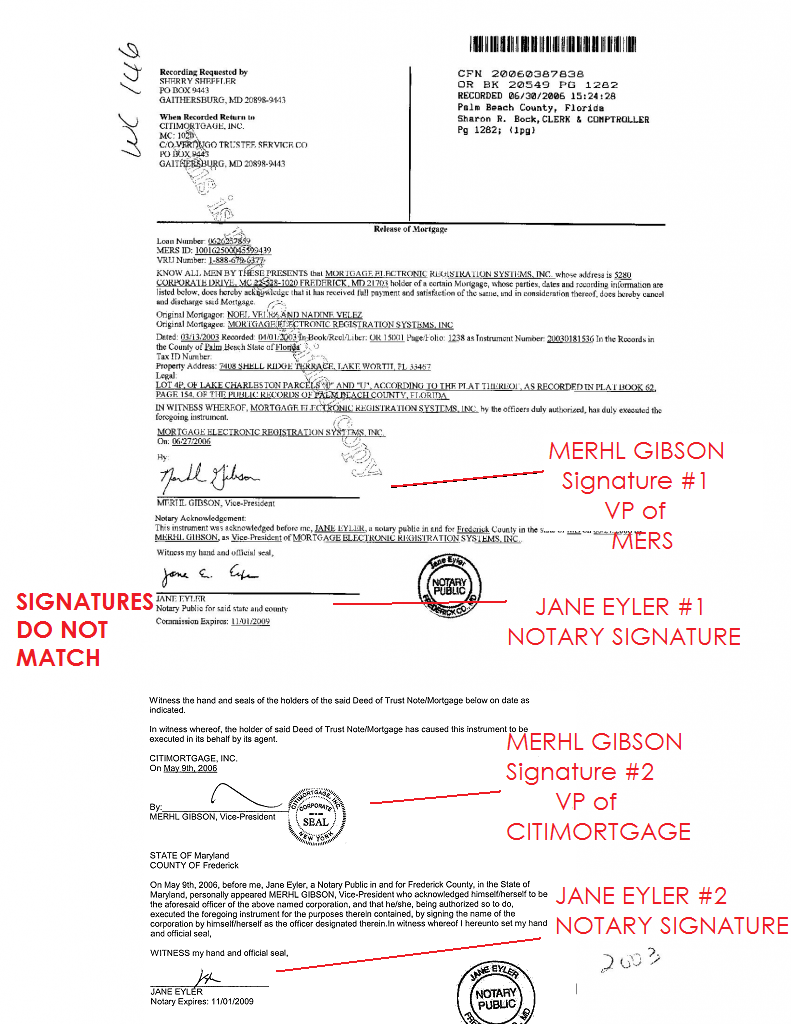
On August 16, 2010, I searched ACRIS and discovered that AHMSI, the successor in interest to plaintiff ARGENT, executed a satisfaction of the instant mortgage almost four months ago, on April 26, 2010. The satisfaction was executed in Idaho Falls, Idaho, by Krystal Hall, Vice President of “AMERICAN HOME MORTGAGE SERVICING, INC., AS SUCCESSOR TO CITI RESIDENTIAL LENDING, INC. AS SUCCESSOR TO ARGENT MORTGAGE COMPANY, LLC,” and the satisfaction was recorded at the Office of the City Register of the City of New York, on May 10, 2010, at CRFN XXXXXXXXXXXXX.
Successor plaintiff AHMSI is one of several companies controlled by billionaire investor Wilbur L. Ross, Jr. through his firm, W. L. Ross & Company. Louise Story, in her April 4, 2008 New York Times article, “Investors Stalk the Wounded of Wall Street,” described Mr. Ross as “a dean of vulture investing.” She wrote:
Almost two centuries ago, as Napoleon marched on Waterloo, a scion of the Rothschilds is said to have declared: The time to buy is when blood is running in the streets.
Now as red ink runs on Wall Street, the figurative heirs of the Rothschilds — bankers, traders, hedge fund gurus and takeover artists — are plotting to profit from today’s financial upheaval. These market opportunists — vulture investors in the Wall Street term — have begun to swoop. They are buying up mortgages of hard-pressed homeowners, the bank loans of cash-short businesses, and companies that seem to be hurtling to bankruptcy. And they are trying to buy them all on the cheap. . . .
“The only time you really know you’ve reached the bottom is when you’re back on the other side and things are going back up,” said Wilbur L. Ross, Jr., a dean of vulture investors, who made a fortune buying steel companies when no one else seemed to want them.
Such caution aside, his firm, W. L. Ross & Company, recently spent $2.6 billion for two mortgage servicers [AHMSI and Option One] and a bond insurance company. He said he planned to buy more as hedge funds and other investor sell at bargain prices.
Moreover, ACRIS revealed that defendant MAITLAND sold the premises to 732 HENDRIX STREET, LLC for $155,000.00, with the deed executed on April 5, 2010 and recorded on April 14, 2010, at the Office of the City Register of the City of New York, at CRFN XXXXXXXXXXXXX.
Plaintiff’s counsel never had the courtesy or professionalism to notify the Court that the instant mortgage was satisfied and file a motion to discontinue the instant action. The Court is gravely concerned that it: expended scarce resources on an action that should have been discontinued; and, would have signed an order that could have possibly damaged the credit rating of defendant MAITLAND and put an unfair cloud on the title to the subject premises now owned by 732 HENDRIX STREET, LLC, causing both defendant MAITLAND and 732 HENDRIX STREET, LLC much time and effort to correct an error caused by the failure of successor plaintiff AHMSI and plaintiff’s counsel to exercise due diligence. If successor plaintiff AHMSI is a responsible lender, not a vulture investor looking to profit “when blood is running in the streets,” it should have notified the Court that the subject mortgage had been satisfied.
Discussion
It is clear that successor plaintiff AHMSI lacked standing to proceed in the instant action since some time prior to April 26, 2010, when the satisfaction for defendant MAITLAND’s mortgage was executed. The exact date is probably April 5, 2010, when defendant MAITLAND likely paid off the subject mortgage loan as part of her closing with 732 HENDRIX STREET, LLC, for the sale of the subject mortgaged premises. “To establish a prima facie case in an action to foreclose a mortgage, the plaintiff must establish the existence of the mortgage and the mortgage note, ownership of the mortgage, and the defendant’s default in payment.” (Campaign v Barba (23 AD3d 327 [2d Dept. 2005]). The instant mortgage was satisfied months before the instant motion for an order of reference was forwarded to me by the Foreclosure Department. The satisfaction, dated April 26, 2010, states that “AMERICAN HOME MORTGAGE INC. AS SUCCESSOR TO CITI RESIDENTIAL LENDING, INC. AS SUCCESSOR TO ARGENT MORTGAGE COMPANY, LLC . . . does hereby certify that a certain indenture of mortgage . . . to secure payment of the principal sum of $392,000.00, and interest, and duly recorded . . . document no. 2006000477619 on the 23rd day of August 2006, is PAID, and does hereby consent that the same be discharged of record.” (See Household Finance Realty Corp. of New York v Wynn, 19 AD3d 545 [2d Dept. 2005]; Sears Mortgage Corp. v Yahhobi, 19 AD3d 402 [2d Dept. 2005]; Ocwen Federal Bank FSB v Miller, 18 AD3d 527 [2d Dept. 2005]; U.S. Bank Trust Nat. Ass’n Trustee v Butti, 16 AD3d 408 [2d Dept 2005]; First Union Mortgage Corp. v Fern, 298 AD2d 490 [2d Dept 2002]; Village Bank v Wild Oaks, Holding, Inc., 196 AD2d 812 [2d Dept 1993]).
The Court of Appeals (Saratoga County Chamber of Commerce, Inc. v Pataki, 100 NY2d 801, 812 [2003], cert denied 540 US 1017 [2003]) declared that “[s]tanding to sue is critical to the proper functioning of the judicial system. It is a threshold issue. If standing is denied, the pathway to the courthouse is blocked. The plaintiff who has standing, however, may cross the threshold and seek judicial redress.”
In Caprer v Nussbaum (36 AD3d 176, 181 [2d Dept 2006]) the Court held that “[s]tanding to sue requires an interest in the claim at issue in the lawsuit that the law will recognize as a sufficient predicate for determining the issue at the litigant’s request.” If a plaintiff lacks standing to sue, the plaintiff may not proceed in the action. (Stark v Goldberg, 297 AD2d 203 [1st Dept 2002]).
Since AHMSI executed the satisfaction for the instant mortgage, the Court must not only deny the instant motion, but also dismiss the complaint and cancel the notice of pendency filed by ARGENT with the Kings County Clerk on November 8, 2007. CPLR § 6501 provides that the filing of a notice of pendency against a property is to give constructive notice to any purchaser of real property or encumbrancer against real property of an action that “would affect the title to, or the possession, use or enjoyment of real property, except in a summary proceeding brought to recover the possession of real property.” Professor David Siegel, in NY Prac, § 334, at 535 [4th ed] observes about a notice of pendency that:
The plaintiff files it with the county clerk of the real property county, putting the world on notice of the plaintiff’s potential rights in the action and thereby warning all comers that if they then buy the property or lend on the strength of it or otherwise rely on the defendant’s right, they do so subject to whatever the action may establish as the plaintiff’s right.
The Court of Appeals, in 5303 Realty Corp. v O & Y Equity Corp. (64 NY2d 313, 315 [1984]), commented that “[a] notice of pendency, commonly known as a lis pendens,‘ can be a potent shield to litigants claiming an interest in real property.” The Court, at 318-320, outlined the history of the doctrine of lis pendens back to 17th century England. It was formally recognized in New York courts in 1815 and first codified in the Code of Procedure [Field Code] enacted in 1848. At 319, the Court stated that “[t]he purpose of the doctrine was to assure that a court retained its ability to effect justice by preserving its power over the property, regardless of whether a purchaser had any notice of the pending suit,” and, at 320, “the statutory scheme permits a party to effectively retard the alienability of real property without any prior judicial review.”
In Israelson v Bradley (308 NY 511, 516 [1955]) the Court observed that with a notice of pendency a plaintiff who has an interest in real property has received from the State:
an extraordinary privilege which . . . upon the mere filing of the notice of a pendency of action, a summons and a complaint and strict compliance with the requirements of section 120 [of the Civil Practice Act; now codified in CPLR § § 6501, 6511 and 6512] is required. Proper administration of the law by the courts requires promptness on the part of a litigant so favored and that he accept the shield which has been given him upon the terms imposed and that he not be permitted to so use the privilege granted that itbecomes a sword usable against the owner or possessor of realty. If the terms imposed are not met, the privilege is at an end. [Emphasis added]
Article 65 of the CPLR outlines notice of pendency procedures. The Court, in Da Silva v Musso (76 NY2d 436, 442 [1990]), held that “the specific statutorily prescribed mechanisms for implementing this provisional remedy . . . were designed with a view toward balancing the interests of the claimant in the preservation of the status quo against the equally legitimate interests of the property owner in the marketability of his title.” The Court of Appeals, quoted Professor Siegel, in holding that “[t]he ability to file a notice of pendency is a privilege that can be lost if abused’ (Siegel, New York Practice § 336, at 512).” (In Re Sakow, 97 NY2d 436, 441 [2002]).
The instant case, with successor plaintiff AHMSI lacking standing to bring this action and the complaint dismissed, meets the criteria for losing “a privilege that can be lost if abused.” CPLR § 6514 (a) provides for the mandatory cancellation of a notice of pendency by:
[t]he court, upon motion of any person aggrieved and upon such notice as it may require, shall direct any county clerk to cancel a notice of pendency, if service of a summons has not been completed within the time limited by section 6512; or if the action has been settled, discontinued or abated; or if the time to appeal from a final judgment against the plaintiff has expired; or if enforcement of a final judgment against the plaintiff has not been stayed pursuant to section 5519. [Emphasis added]
The plain meaning of the word “abated,” as used in CPLR § 6514 (a) is the ending of an action. Abatement is defined (Black’s Law Dictionary 3 [7th ed 1999]) as “the act of eliminating or nullifying.” “An action which has been abated is dead, and any further enforcement of the cause of action requires the bringing of a new action, provided that a cause of action remains’ (2A Carmody-Wait 2d § 11.1).” (Nastasi v Nastasi, 26 AD3d 32, 40 [2d Dept 2005]). Further, Nastasi at 36, held that “[c]ancellation of a notice of pendency can be granted in the exercise of the inherent power of the court where its filing fails to comply with CPLR 6501 (see 5303 Realty Corp. v O & Y Equity Corp. at 320-321; Rose v Montt Assets, 250 AD2d 451, 451-452 [1st Dept 1998]; Siegel, NY Prac § 336 [4th ed]).” AHMSI, as successor plaintiff, lacks standing to sue. Therefore, dismissal of the instant complaint must result in mandatory cancellation of the November 8, 2007 notice of pendency against the property “in the exercise of the inherent power of the Court.”
The failure of successor plaintiff AHMSI, by its President David M. Friedman or its Executive Vice President, Chief Legal Officer and Secretary Jordan D. Dorchuck, Esq., and its counsel, Melissa A. Sposato, Esq. and her firm, Jordan S. Katz, P.C., to discontinue the instant action since the April 2010 payoff of the MAITLAND mortgage appears to be “frivolous.” 22 NYCRR § 130-1.1 (a) states that “the Court, in its discretion may impose financial sanctions upon any party or attorney in a civil action or proceeding who engages in frivolous conduct as defined in this Part, which shall be payable as provided in section 130-1.3 of this Subpart.” Further, it states in 22 NYCRR § 130-1.1 (b), that “sanctions may be imposed upon any attorney appearing in the action or upon a partnership, firm or corporation with which the attorney is associated.”
22 NYCRR § 130-1.1 (c) states that:
For purposes of this part, conduct is frivolous if:
(1) it is completely without merit in law and cannot be supported by a reasonable argument for an extension, modification or reversal of existing law;
(2) it is undertaken primarily to delay or prolong the resolution of the litigation, or to harass or maliciously injure another; or
(3) it asserts material factual statements that are false.
It is clear that since at least April 26, 2010 the instant motion for aan order of reference “is completely without merit in law” and “asserts material factual statements that are false.”
Several years before the drafting and implementation of the Part 130 Rules for costs and sanctions, the Court of Appeals (A.G. Ship Maintenance Corp. v Lezak, 69 NY2d 1, 6 [1986]) observed that “frivolous litigation is so serious a problem affecting the proper administration of justice, the courts may proscribe such conduct and impose sanctions in this exercise of their rule-making powers, in the absence of legislation to the contrary (see NY Const, art VI, § 30, Judiciary Law § 211 [1] [b] ).”
Part 130 Rules were subsequently created, effective January 1, 1989, to give the courts an additional remedy to deal with frivolous conduct. These stand beside Appellate Division disciplinary case law against attorneys for abuse of process or malicious prosecution. The Court, in Gordon v Marrone (202 AD2d 104, 110 [2d Dept 1994], lv denied 84 NY2d 813 [1995]), instructed that:
Conduct is frivolous and can be sanctioned under the court rule if “it is completely without merit . . . and cannot be supported by a reasonable argument for an extension, modification or reversal of existing law; or . . .
it is undertaken primarily to delay or prolong the resolution of the litigation, or to harass or maliciously injure another” (22 NYCRR 130-1.1[c] [1], [2] . . . ).
In Levy v Carol Management Corporation (260 AD2d 27, 33 [1st Dept 1999]) the Court stated that in determining if sanctions are appropriate the Court must look at the broad pattern of conduct by the offending attorneys or parties. Further, “22 NYCRR 130-1.1 allows us to exercise our discretion to impose costs and sanctions on an errant party . . .” Levy at 34, held that “[s]anctions are retributive, in that they punish past conduct. They also are goal oriented, in that they are useful in deterring future frivolous conduct not only by the particular parties, but also by the Bar at large.”
The Court, in Kernisan, M.D. v Taylor (171 AD2d 869 [2d Dept 1991]), noted that the intent of the Part 130 Rules “is to prevent the waste of judicial resources and to deter vexatious litigation and dilatory or malicious litigation tactics (cf. Minister, Elders & Deacons of Refm. Prot. Church of City of New York v 198 Broadway, 76 NY2d 411; see Steiner v Bonhamer, 146 Misc 2d 10) [Emphasis added].” Since at least April 26, 2010, and probably since April 5, 2010, the instant action is “a waste of judicial resources.” This conduct, as noted in Levy, must be deterred. In Weinstock v Weinstock (253 AD2d 873 [2d Dept 1998]) the Court ordered the maximum sanction of $10,000.00 for an attorney who pursued an appeal “completely without merit,” and holding, at 874, that “[w]e therefore award the maximum authorized amount as a sanction for this conduct (see, 22 NYCRR 130-1.1) calling to mind that frivolous litigation causes a substantial waste of judicial resources to the detriment of those litigants who come to the Court with real grievances [Emphasis added].” Citing Weinstock, the Appellate Division, Second Department, in Bernadette Panzella, P.C. v De Santis (36 AD3d 734 [2d Dept 2007]) affirmed a Supreme Court, Richmond County $2,500.00 sanction, at 736, as “appropriate in view of the plaintiff’s waste of judicial resources [Emphasis added].”
In Navin v Mosquera (30 AD3d 883 [3d Dept 2006]) the Court instructed that when considering if specific conduct is sanctionable as frivolous, “courts are required to examine whether or not the conduct was continued when its lack of legal or factual basis was apparent [or] should have been apparent’ (22 NYCRR 130-1.1 [c]).” The Court, in Sakow ex rel. Columbia Bagel, Inc. v Columbia Bagel, Inc. (6 Misc 3d 939, 943 [Sup Ct,
New York County 2004]), held that “[i]n assessing whether to award sanctions, the Court must consider whether the attorney adhered to the standards of a reasonable attorney (Principe v Assay Partners, 154 Misc 2d 702 [Sup Ct, NY County 1992]).” In the instant action, plaintiff’s Chief Legal Officer or its outside counsel is responsible for keeping track of whether the mortgage was satisfied. In Sakow at 943, the Court observed that “[a]n attorney cannot safely delegate all duties to others.”
This Court will examine the conduct of successor plaintiff AHMSI and plaintiff’s counsel, in a hearing, pursuant to 22 NYCRR § 130-1.1, to determine if plaintiff AHMSI, by its President, David M. Friedman, or its Executive Vice President, Chief Legal Officer and Secretary, Jordan D. Dorchuck, Esq., and plaintiff’s counsel Melissa A. Sposato, Esq. and her firm Jordan S. Katz, P.C. engaged in frivolous conduct, and to allow successor plaintiff AHMSI, by its President David M. Friedman or Executive Vice President, Chief Legal Officer and Secretary Jordan D. Dorchuck, Esq., and plaintiff’s counsel Melissa A. Sposato, Esq. and her firm Jordan S. Katz, P.C. a reasonable opportunity to be heard. The Court is aware that AHMSI’s Chief Legal Officer, Mr. Dorchuck, is a member of the New York State Bar. (See Mascia v Maresco, 39 AD3d 504 [2d Dept 2007]; Yan v Klein, 35 AD3d 729 [2d Dept 2006]; Greene v Doral Conference Center Associates, 18 AD3d 429 [2d Dept 2005]; Kucker v Kaminsky & Rich, 7 AD3d 39 [2d Dept 2004]).
Conclusion
Accordingly, it is
ORDERED, that the motion of successor plaintiff, AMERICAN HOME MORTGAGE SERVICING, INC., for an order of reference for the premises located at 732 Hendrix Street, Brooklyn, New York (Block 4305, Lot 22, County of Kings), is denied with prejudice; and it is further
ORDERED, that because successor plaintiff, AMERICAN HOME MORTGAGE SERVICING, INC., lacks standing and no longer is the mortgagee in this foreclosure action, the instant complaint, Index No. 41383/07 is dismissed with prejudice; and it is further
ORDERED, that the Notice of Pendency filed with the Kings County Clerk on November 8, 2007, by original plaintiff, ARGENT MORTGAGE COMPANY, LLC, in an action to foreclose a mortgage for real property located at 732 Hendrix Street, Brooklyn, New York (Block 4305, Lot 22, County of Kings), is cancelled; and it is further
ORDERED, that it appearing that successor plaintiff AMERICAN HOME MORTGAGE SERVICING, INC., Melissa A. Sposato, Esq. and Jordan S. Katz, P.C. engaged in “frivolous conduct,” as defined in the Rules of the Chief Administrator, 22 NYCRR § 130-1 (c), and that pursuant to the Rules of the Chief Administrator, 22 NYCRR § 130.1.1 (d), “[a]n award of costs or the imposition of sanctions may be made. . . upon the court’s own initiative, after a reasonable opportunity to be heard,” this Court will conduct a hearing affording: successor plaintiff AMERICAN HOME MORTGAGE SERVICING, INC., by its President David M. Friedman or Executive Vice President, Chief Legal Officer and Secretary, Jordan D. Dorchuck, Esq.; Melissa A. Sposato, Esq.; and, Jordan S. Katz, P.C.; “a reasonable opportunity to be heard” before me in Part 27, on Monday, September 13, 2010, at 2:30 P.M., in Room 479, 360 Adams Street, Brooklyn, NY 11201; and it is further
ORDERED, that because the headquarters of successor plaintiff AMERICAN HOME MORTGAGE SERVICING, INC. is in Irving, Texas, Mr. Friedman or Mr. Dorchuck may appear either in person or by telephone; and it is further
ORDERED, that Ronald David Bratt, Esq., my Principal Law Clerk, is directed to serve this order by first-class mail, upon: David M. Friedman, President of successor plaintiff AMERICAN HOME MORTGAGE SERVICING, INC., 4600 Regent Boulevard, Suite 200, Irving, Texas 75063; Jordan D. Dorchuck, Esq., Executive Vice President, Chief Legal Officer and Secretary of successor plaintiff AMERICAN HOME MORTGAGE SERVICING, INC., 4600 Regent Boulevard, Suite 200, Irving, Texas 75063; Melissa A. Sposato, Esq., Law Offices of Jordan S. Katz, P.C., 395 North Service Road, Suite 401, Melville, New York XXXXX-XXXX; and Jordan S. Katz, P.C., 395 North Service Road, Suite 401, Melville, New York XXXXX-XXXX.
This constitutes the Decision and Order of the Court.
© 2010-19 FORECLOSURE FRAUD | by DinSFLA. All rights reserved.
Be sure to go to the link below to see the fraud I uncovered in the Shapiro’s case mentioned in this PB Post article!
 Continue reading…PALM BEACH POST
Continue reading…PALM BEACH POST














Recent Comments