against
Ellen N. Taher, et. al., Defendants.
9320/09
Appearances:
Plaintiff
William G. Kelly, Esq.
Frank Cassara, Esq.
Shapiro DiCaro and Barak, LLC
Rochester NY
Michael O. Ware, Esq.
Mayer Brown, LLP
NY NY
Marco Cercone, Esq.
Ruup Baase Pfalzgraf Cunningham and Coppola
Buffalo NY
Defendant No Appearance
Arthur M. Schack, J.
The following papers numbered 1 – 7 read on this decision:Papers Numbered:
Affidavits with or without Exhibits1, 2, 3, 4
Memoranda of Law_________________________________5, 6
Transcript of July 15, 2011 Court Proceedings____________7
________________________________________________________________________
The Court, in this dismissed foreclosure action, pursuant to 22 NYCRR § 130-1.1 (a), imposes the following sanctions for “frivolous conduct,” in violation of 22 NYCRR
§ 130-1.1 (c): the maximum sanction of $10,000.00 upon plaintiff, HSBC BANK USA, N.A., AS INDENTURE TRUSTEE FOR THE REGISTERED NOTEHOLDERS OF RENAISSANCE HOME EQUITY LOAN TRUST 2007-2 (HSBC), because HSBC’s use of robosigners in the instant action “is completely without merit in law,” HSBC “asserts material factual statements that are false” and HSBC’s continuation of the action with all its defects is a waste of judicial resources; and, a sanction of $5,000.00 upon HSBC’s counsel, Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC, because Frank M. Cassara, Esq., of Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC “asserts material factual statements that are false” and Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC’s continuation of the action with all its defects is a waste of judicial resources. The Court is not imposing a sanction upon Frank M. Cassara, Esq. because, pursuant to 22 NYCRR § 130-1.1 (b), the sanction is imposed upon Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC, the “firm . . . with which the attorney is associated.”
The frivolous conduct of HSBC and Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC is detailed in my prior decision and order in this action (32 Misc 3d 1208 (A) [July 1, 2011]). Further, I conducted a hearing on July 15, 2011, to give HSBC, Frank M. Cassara, Esq. and Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC a “a reasonable opportunity to be heard” before any imposition of sanctions, pursuant to 22 NYCRR § 130-1.1 (d).
This decision and order is based upon my review of the minutes of the July 15, 2011 Part 130 hearing, my prior orders and decisions in the instant matter and my review of affidavits and memoranda of law submitted by counsel for HSBC and Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC. Therefore, pursuant to 22 NYCRR § 130-1.2, this is the “written decision setting forth the conduct on which the award or imposition [of sanctions] is based, the reasons why the court found the conduct to be frivolous, and the reasons why the court found the amount awarded or imposed to be appropriate.”
Background
Plaintiff HSBC moved in this foreclosure action, upon the default of all defendants, for an order of reference and related relief for the premises located at 931 Gates Avenue, Brooklyn, New York (Block 1632, Lot 57, County of Kings). On November 8, 2010, I issued a decision and order instructing plaintiff’s counsel, Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC, to comply with the affirmation requirements of Administrative Order 548/10, issued, on October 20, 2010, by then Chief Administrative Judge Ann T. Pfau. Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC was ordered to submit the required affirmation “within sixty (60) days of this decision and order, or the instant foreclosure action will be dismissed with prejudice.” Moreover, my decision and order mandated, with respect to the attorney’s affirmation, that: [*2]
plaintiff’s counsel to state that he communicated on a specific date
with a named representative of plaintiff HSBC who informed counsel
that he or she:
(a) has personally reviewed plaintiff’s documents and records
relating to this case; (b) has reviewed the Summons and
Complaint, and all other papers filed in this matter in support
of foreclosure; and, (c) has confirmed both the factual accuracy
of these court filings and the accuracy of the notarizations
contained therein.
Further, plaintiff’s counsel, based upon his or her communication
with plaintiff’s representative named above must upon his or her
“inspection of the papers filed with the Court and other diligent
inquiry, . . . certify that, to the best of [his or her] knowledge, information
and belief, the Summons and Complaint filed in support of this action
for foreclosure are complete and accurate in all relevant respect.”
Counsel is reminded that the new standard Court affirmation form
states in a note at the top of the first page:
During and after August 2010, numerous and widespread
insufficiencies in foreclosure filings in various courts around the
nation were reported by major mortgage lenders and other authorities.
These insufficiencies include: failure of plaintiffs and their counsel
to review documents and files to establish standing and other foreclosure requisites; filing of notarized affidavits which falsely attest to such
review and to other critical facts in the foreclosure process; and
“robosigning” of documents by parties and counsel. The wrongful
filing and prosecution of foreclosure proceedings which are discovered
to suffer from these defects may be cause for disciplinary and other
sanctions upon participating counsel. [Emphasis added]
The Office of Court Administration, in its October 20, 2010 press release about the
new affirmation requirement, stated that the new attorney affirmation filing requirement was instituted:
to protect the integrity of the foreclosure process and prevent wrongful foreclosures . . . The new filing requirement was introduced by the Chief [*3]
Judge in response to recent disclosures by major mortgage lenders of
significant insufficiencies — including widespread deficiencies in
notarization and “robosigning” of supporting documents — in residential
foreclosure filings in courts nationwide . . .
Chief Judge Lippman said, “We cannot allow the courts
in New York State to stand by idly and be party to what we now
know is a deeply flawed process, especially when that process
involves basic human needs — such as a family home — during
this period of economic crisis. This new filing requirement will
play a vital role in ensuring that the documents judges rely on will
be thoroughly examined, accurate, and error-free before any judge
is asked to take the drastic step of foreclosure.” [Emphasis added]
On January 7, 2011, HSBC’s deadline day to submit the required affirmation, Mr.
Cassara, of Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC, submitted to my chambers the required affirmation. Mr. Cassara, affirmed “under the penalties of perjury”:
2. On January 4, 2011 and January 5, 2011, I communicated with
the following representative or representatives of Plaintiff, who informed
me that he/she/they (a) personally reviewed plaintiff’s documents and
records relating to this case for factual accuracy; and (b) confirmed
the factual accuracy and allegations set forth in the Complaint and
any supporting affirmations filed with the Court, as well as the accuracy
of the notarizations contained in the supporting documents filed there with.
Name Title
Christina Carter Manager of Account Management
3. Based upon my communication with Christina Carter, as well
as upon my inspection and reasonable inquiry under the circumstances,
I affirm that, to the best of my knowledge, information, and belief, the
Summons and Complaint, and other papers filed or submitted to the
Court in this matter contain no false statements of fact or law . . .
4. I am aware of my obligations under New York Rules of Professional
Conduct (22 NYCRR Part 1200) and 22 NYCRR Part 130. [Emphasis [*4]
added]
However, the Court discovered problems with Mr. Cassara’s affirmation and the subject foreclosure action. Plaintiff HSBC lacked standing to commence the instant foreclosure action because the assignment to HSBC of the subject mortgage and note by MORTGAGE ELECTRONIC REGISTRATION SYSTEMS, INC. (MERS) was without legal authority. MERS never possessed the TAHER note it allegedly assigned to plaintiff HSBC. Therefore, the Court dismissed the instant action with prejudice because HSBC did not have standing to commence the action.
Then, I held at * 2-3, of my July 1, 2011 decision and order:
Mr. Cassara’s affirmation, affirmed “under the penalties of
perjury,” that to the best of Mr. Cassara’s “knowledge, information,
and belief, the Summons and Complaint, and other papers filed or
submitted to the Court in this matter contain no false statements of
fact or law,” is patently false. Moreover, the Court is troubled that:
the alleged representative of plaintiff HSBC, Christina Carter, who
according to Mr. Cassara, “confirmed the factual accuracy and
allegations set forth in the Complaint and any supporting affirmations
filed with the Court, as well as the accuracy of the notarizations
contained in the supporting documents filed therewith,“is not an
employee of HSBC, but a robosigner employed by OCWEN LOAN
SERVICING, LLC [OCWEN], whose signature on legal documents
has at least three variations; the MERS to plaintiff HSBC assignment
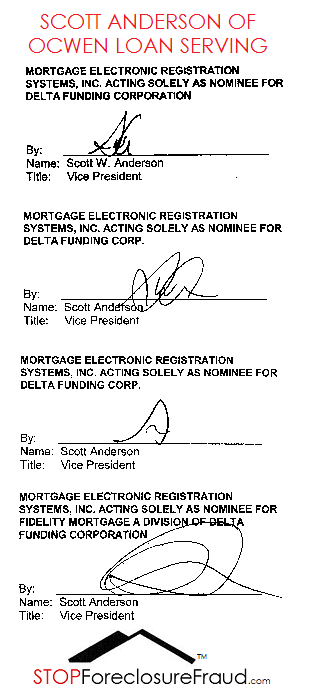
of the subject mortgage and note was executed by Scott W. Anderson,
a known robosigner and OCWEN employee, whose signature is
reported to have appeared in at least four different variations on
mortgage assignments; and, the instant affidavit of merit was executed
by Margery Rotundo, another robosigner, OCWEN employee and self-
alleged employee of various other banking entities . . .
Last month, on May 19, 2011, in a case involving a defective
MERS to HSBC assignment by a robosigner, Maine’s highest court,
the Supreme Judicial Court, found that HSBC’s affidavits and the
assignment of the note and mortgage by MERS to HSBC contained
serious defects. The Maine Court held “that the affidavits submitted [*5]
by HSBC contain serious irregularities that make them inherently
untrustworthy.” (HSBC Mortg. Services, Inc. v Murphy, 19 A3d 815,
820). HSBC has a history of foreclosure actions before me with
affidavits of merit executed by Margery Rotundo and MERS to
HSBC assignments executed by Scott Anderson that “contain serious
irregularities that make them inherently untrustworthy.” Moreover,
Mr. Cassara was put on notice, in my November 8, 2010 decision and
order, that “[t]he wrongful filing and prosecution of foreclosure
proceedings which are discovered to suffer from these defects may
be cause for disciplinary and other sanctions upon participating counsel.”
Moreover, in my July 1, 2011 decision and order, at * 3, I emphasized to plaintiff HSBC’s counsel that:
Chief Judge Jonathan Lippman, in the Office of Court
Administration’s October 20, 2010 press release about the issuance of
Administrative Order 548/10 and the need for plaintiff’s counsel in
foreclosure actions to verify the accuracy of supporting documents,
stated that “[w]e cannot allow the courts in New York State to stand by
idly and be party to what we now know is a deeply flawed process,
especially when that process involves basic human needs — such as
a family home — during this period of economic crisis.” Frivolous
conduct, as defined by 22 NYCRR § 130.1.1 (c), includes conduct that
“is completely without merit in law” and “asserts material factual
statements that are false.” Further, the Part 130 rules are intended to
stop the waste of judicial resources, which appears to have occurred in
the TAHER foreclosure action. In the instant action: the assignment of
the subject mortgage and note by MERS to HSBC is without legal
authority; HSBC’s continued use of robo-signers “is completely without
merit in law”; plaintiff HSBC “asserts material factual statements that
are false”; and, the continuation of this case with all its defects is a
waste of judicial resources. Therefore, plaintiff HSBC’s President and
Chief Executive Officer, Irene M. Dorner, its counsel, Frank M. Cassara, [*6]
Esq., and his firm, Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC, will be given an
opportunity to be heard why this Court should not sanction them for
making a “frivolous motion,” pursuant to 22 NYCRR §130-1.1.
In my July 1, 2011 decision and order, I found that defendant TAHER’s lender, DELTA FUNDING CORPORATION (DELTA), pursuant to the terms of a consolidation, extension and modification agreement, not MERS, was the “Note Holder.” Despite this, MERS assigned DELTA’s consolidation, extension and modification agreement and note to HSBC, in an assignment executed by Scott W. Anderson, as “Senior Vice President of Residential Loan Servicing” for “MORTGAGE ELECTRONIC REGISTRATIONS SYSTEMS, INC., as nominee for DELTA FUNDING CORPORATION by its attorney-in-fact OCWEN LOAN SERVING, LLC.” I noted that both assignor MERS and assignee HSBC have the same address, 1661 Worthington Road, Suite 100, West Palm Beach, FL 33409, which is OCWEN’s address. Also, Mr.
Anderson’s assignment referred to a recorded power of attorney from DELTA to OCWEN, which upon my inspection proved to be a limited power of attorney from DELTA to OCWEN for a different address.
With respect to robosigner Scott Anderson, I observed in my July 1, 2011 decision and order, at * 5, that:
the Ohio Court of Appeals, Second District, Montgomery County
(2010 WL 3451130, 2010-Ohio-4158, lv denied 17 Ohio St.3d 1532
[2011]), affirmed the denial of a foreclosure, sought by plaintiff
HSBC, because of numerous irregularities. The Ohio Court, in
citing four decisions by this Court [three of the four involved Scott
Anderson as assignor] summarized some of this Court’s prior concerns
with HSBC and Mr. Anderson, in observing, at * 11:
recent decisions in the State of New York have noted numerous
irregularities in HSBC’s mortgage documentation and corporate
relationships with Ocwen, MERS, and Delta. See, e.g., HSBC
Bank USA, N.A. v Cherry (2007), 18 Misc 3d 1102 (A) [Scott
Anderson assignor] and HSBC Bank USA, N.A. v Yeasmin
(2010), 27 Misc 3d 1227 (A) (dismissing HSBC’s requests for
orders of reference in mortgage foreclosure actions, due to
HSBC’s failure to provide proper affidavits). See, also, e.g.,
HSBC Bank USA, N.A. v Charlevagne (2008), 20 Misc 3d
1128 (A) [Scott Anderson assignor] and HSBC Bank USA,
N.A. v Antrobus (2008), 20 Misc 3d 1127 (A) [Scott Anderson
assignor] (describing “possible incestuous relationship” between
HSBC Bank, Ocwen Loan Servicing, Delta Funding Corporation, [*7]
and Mortgage Electronic Registration Systems, Inc., due to the fact
that the entities all share the same office space at 1661 Worthington
Road, Suite 100, West Palm Beach, Florida. HSBC also supplied
affidavits in support of foreclosure from individuals who
claimed simultaneously to be officers of more than one of these corporations.).
I reviewed Scott Anderson’s signature in the instant MERS to HSBC assignment and then went to the Automated City Register Information System (ACRIS) of the New York City Register to compare Mr. Anderson’s signature with that used in five prior Scott Anderson foreclosure cases decided by this Court. I found that Mr. Anderson used five variations of his initials, “SA,” but never signed his name in full.
Also, I found that Margery Rotundo, who executed the April 27, 2009 affidavit of merit and amount due in the instant action, at * 7 of my July 1, 2011 decision and order, had “in prior foreclosure cases before me, a history of alleging to be the Senior Vice President of various entities, including plaintiff HSBC, Nomura Credit & Capital, Inc. and an unnamed servicing agent for HSBC. In the instant action she claims to be the Senior Vice President of Residential Loss Mitigation of OCWEN, HSBC’s servicing agent.”
Then, with respect to Christina Carter, at * 8 of my July 1, 2011 decision and order, I observed:
Mr. Cassara, plaintiff’s counsel affirmed that “On January 4,
2011 and January 5, 2011, I communicated with the following
representative . . . of Plaintiff . . . Christina Carter . . . Manager of
Account Management.” This is disingenuous. Ms. Carter is not
employed by plaintiff, but by OCWEN. She executed documents as
an officer of MERS and as an employee of OCWEN. Ms. Carter’s
signature on documents is suspect because of the variations of her
signature used.
This Court examined eight recent documents that exhibit
three different variations of Christina Carter’s signature.
In my July 1, 2011 decision and order, I explained in detail why HSBC failed to have standing to assign the subject mortgage and note, holding at * 10, that “[i]n the instant action, even if MERS had authority to transfer the mortgage to HSBC, DELTA, not MERS, is the note holder. Therefore, MERS cannot transfer something it never proved it possessed.” I cited Aurora Loan Services, LLC v Weisblum (85 AD3d 95, 108 [2d Dept May 14, 2011]), which holds:
In order to commence a foreclosure action, the plaintiff must
have a legal or equitable interest in the mortgage (see Wells Fargo
Bank, N.A. v Marchione, 69 AD3d, 204, 207 [2d Dept 2009]). A
plaintiff has standing where it is both (1) the holder or assignee of
the subject mortgage and (2) the holder or assignee of the underlying
note, either by physical delivery or execution of a written assignment
prior to the commencement of the action with the filing of the complaint
(see Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. v Marchione, 69 AD3d at 207-209; U.S. [*8]
Bank v Collymore, 68 AD3d 752, 754 [2d Dept 2009].)
Moreover, in my July 1, 2011 decision and order, with respect to the authority of MERS as nominee to assign a mortgage and note, I held, at * 10:
Scott Anderson for MERS as assignor, did not have specific
authority to sign the TAHER mortgage. Under the terms of the
consolidation, extension and modification agreement, MERS is
“acting solely as nominee for Lender [DELTA].” The alleged power
of attorney cited in the Scott Anderson MERS to HSBC assignment,
as described above, is a limited power of attorney from DELTA to
OCWEN for the premises located at 14 Harden Street, Brooklyn,
New York, not the subject premises. MERS is not mentioned or
involved with this limited power of attorney. In both underlying
TAHER mortgages MERS was “acting solely as a nominee for
Lender,” which is DELTA. The term “nominee” is defined as “[a]
person designated to act in place of another, usu. in a very limited
way” or “[a] party who holds bare legal title for the benefit of others.”
(Black’s Law Dictionary 1076 [8th ed 2004]). “This definition suggests
that a nominee possesses few or no legally enforceable rights beyond
those of a principal whom the nominee serves.” (Landmark National Bank v Kesler, 289 Kan 528, 538 [2009]).
Then, I held, at * 12-13 of my July 1, 2011 decision and order, that MERS, as DELTA’s nominee, its agent for limited purposes, lacked authority to assign the TAHER consolidation, extension and modification agreement, because:
several weeks ago, the Appellate Division, Second Department in
Bank of New York v Silverberg, (86 AD3d 274 [June 7, 2011]),
confronted the issue of “whether a party has standing to commence
a foreclosure action when that party’s assignor—in this case, Mortgage
Electronic Registration Systems, Inc. (hereinafter MERS)—was listed
in the underlying mortgage instruments as a nominee and mortgagee
for the purpose of recording, but was never the actual holder or
assignee of the underlying notes.” The Court held, “[w]e answer
this question in the negative.” Silverberg, similar to the instant [*9]
TAHER matter, deals with the foreclosure of a mortgage with a
consolidation, modification and extension agreement. MERS, in
the Silverberg case and the instant TAHER action, never had title
or possession of the Note and the definition of “Note Holder” is
substantially the same in both consolidation, extension and modification agreements. The Silverberg Court instructed, at 281-282:
the assignment of the notes was thus beyond MERS’s authority
as nominee or agent of the lender (see Aurora Loan Servs.,
LLC v Weisblum, 2011 NY Slip Op 04184, *6-7 [2d Dept
2011]; HSBC Bank USA v Squitteri, 29 Misc 3d 1225 [A]
[Sup Ct, Kings County, F. Rivera, J.]; ; LNV Corp. v Madison
Real Estate, LLC, 2010 NY Slip Op 33376 [U] [Sup Ct, New
York County 2010, York, J.]; LPP Mtge. Ltd. v Sabine Props.,
LLC, 2010 NY Slip Op 32367 [U] [Sup Ct, New York County
2010, Madden, J.]; Bank of NY v Mulligan, 28 Misc 3d 1226 [A]
[Sup Ct, Kings County 2010, Schack, J.]; One West Bank,
F.S.B., v Drayton, 29 Misc 3d 1021[Sup Ct, Kings County
2010, Schack, J.]; Bank of NY v Alderazi, 28 Misc 3d 376,
379-380 [Sup Ct, Kings County 2010, Saitta, J.] [the “party
who claims to be the agent of another bears the burden of
proving the agency relationship by a preponderance of the
evidence”]; HSBC Bank USA v Yeasmin, 24 Misc 3d 1239 [A]
[Sup Ct, Kings County 2010, Schack, J.]; HSBC Bank USA,
N.A. v Vasquez, 24 Misc 3d 1239 [A], [Sup Ct, Kings County
2009, Schack, J.]; Bank of NY v Trezza, 14 Misc 3d 1201 [A]
[Sup Ct, Suffolk County 2006, Mayer, J.]; La Salle Bank Natl.
Assn. v Lamy, 12 Misc 3d 1191 [A] [Sup Ct, Suffolk County,
2006, Burke, J.]; Matter of Agard, 444 BR 231 [Bankruptcy
Court, ED NY 2011, Grossman, J.]; but see U.S. Bank N.A. v
Flynn, 27 Misc 3d 802 [Sup Ct, Suffolk County 2011, Whelan,
J.]).
Moreover, the Silverberg Court concluded, at 283, that “because [*10]
MERS was never the lawful holder or assignee of the notes described
and identified in the consolidation agreement, the . . . assignment of
mortgage is a nullity, and MERS was without authority to assign the
power to foreclose to the plaintiff. Consequently, the plaintiff failed
to show that it had standing to foreclose.” Further, the Silverberg
Court observed, at 283, “the law must not yield to expediency and
the convenience of lending institutions. Proper procedures must
be followed to ensure the reliability of the chain of ownership, to secure
the dependable transfer of property, and to assure the enforcement of
the rules that govern real property.” [Emphasis added]
Therefore, the instant action is dismissed with prejudice.
Thus, because of: the defects found in Mr. Cassara’s January 6, 2011 affirmation,
affirmed, “under the penalties of perjury”; the warning to plaintiff’s counsel that “[t]he wrongful filing and prosecution of foreclosure proceedings which are discovered to suffer from these defects may be cause for disciplinary and other sanctions upon participating counsel”; plaintiff HSBC’s lack of standing to bring the instant action; plaintiff HSBC’s complaint being replete with false statements, such as alleging its offices were located at 1661 Worthington Road, Suite 100, West Palm Beach, FL 33409, which is actually OCWEN’s office, and that it owned the TAHER note, which it did not; the use in the instant foreclosure of three robosigners – Scott Anderson, Margery Rotundo and Christina Carter; and, the waste of judicial resources, in this matter, with defective paperwork and robosigners; I ordered, at * 17, of my July 1, 2011 decision and order, that:
the Court will examine the conduct of plaintiff HSBC and plaintiff’s
counsel, in a hearing, pursuant to 22 NYCRR § 130-1.1, to determine
if plaintiff HSBC, by its President and CEO, Irene M. Dorner, and
plaintiff’s counsel Frank M. Cassara, Esq. and his firm Shapiro, DiCaro
& Barak, LLC, engaged in frivolous conduct, and to allow plaintiff
HSBC, by its President and CEO, Irene M. Dorner, and plaintiff’s
counsel Frank M. Cassara, Esq. and his firm Shapiro, DiCaro &
Barak, LLC a reasonable opportunity to be heard.
With respect to HSBC’s President and CEO, Irene M. Dorner, I noted, at * 17 of my July 1, 2011 decision and order:
plaintiff HSBC’s President and Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
bears a measure of responsibility for plaintiff’s actions, as well as
plaintiff’s counsel . . . Dorner . . . is HSBC’s “captain of the ship.”
She should not only take credit for the fruits of HSBC’s victories but
must bear some responsibility for its defeats and mistakes. According
to HSBC’s 2010 Form 10-K, dated December 31, 2010, and filed with
the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission on February 28, 2011, [*11]
at p. 255, “Ms. Dorner’s insight and particular knowledge of HSBC
USA’s operations are critical to an effective Board of Directors” and
Ms. Dorner “has many years of experience in leadership positions
with HSBC and extensive global experience with HSBC, which is
highly relevant as we seek to operate our core businesses in support
of HSBC’s global strategy.” HSBC needs to have a “global strategy”
of filing truthful documents and not wasting the very limited resources
of the Courts. For her responsibility she earns a handsome compensation
package. According to the 2010 Form 10-K, at pp. 276-277, she earned
in 2010 total compensation of $2,306,723. This included, among other
things: a base salary of $566,346; a discretionary bonus of $760,417;
and, other compensation such as $560 for financial planning and
executive tax services; $40,637 for executive travel allowance,
$24,195 for housing and furniture allowance, $39,399 for relocation
expenses and $3,754 for executive physical and medical expenses.
Opposition papers to sanctions
OCWEN, as attorney-in-fact for HSBC, on July 12, 2011, substituted Ruppe, Baase, Pfalzgraf, Cunningham, Coppola, LLC for Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC, as counsel for HSBC. Ruppe, Baase, Pfalzgraf, Cunningham, Coppola, LLC submitted to the Court papers opposing sanctions against HSBC.
However, it appears to the Court that HSBC was never notified by OCWEN or Ruppe, Baase, Pfalzgraf, Cunningham, Coppola, LLC that they were being represented at the July 15, 2011 hearing. On July 15, 2011, at about 12:40 P.M., less than two hours before the sanctions hearing was scheduled to commence, a messenger from the “white-shoe” law firm Mayer Brown, LLP delivered to my chambers, an affidavit, with exhibits, executed that day by Thomas Musarra, alleging to be “a senior vice president of HSBC Bank USA” and “the head of HSBC’s Corporate Trust and Loan Agency Transaction Management Department, the unit responsible for HSBC’s work as trustee or indenture trustee in residential mortgage-backed securities transactions.” Mr. Mussara “being duly sworn” states, in ¶ 4, of his affidavit that “[m]y department has no record of the loan to defendant Eileen Taher being brought to our attention by the Servicer [OCWEN] or otherwise until last week.” Michael Ware, Esq., of Mayer Brown, LLP, in his Memorandum of Law, attached to the Musarra affidavit, claims that his Memorandum of Law was submitted for HSBC and Irene M. Dorner “in its corporate capacity and not as Indenture Trustee for the Registered Noteholders of Renaissance Home Equity Loan Trust 2007-2.”
However, Mayer Brown, LLP, pursuant to CPLR § 1013, never moved by motion to intervene in the instant action for HSBC “in its corporate capacity and not as Indenture Trustee for the Registered Noteholders of Renaissance Home Equity Loan Trust 2007-2,” if that is even possible. The poet Gertrude Stein wrote in Sacred Emily that a “Rose is a rose is a rose is a rose” and William Shakespeare wrote in Romeo and Juliet that “A rose by any other name would smell as sweet.” HSBC, whether in its corporate capacity or as an Indenture Trustee, is HSBC, whether it smells sweet or otherwise. Therefore, HSBC is HSBC is HSBC is HSBC.
Goldberg Segalla, LLP represented Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC and Frank M. Cassara, [*12]Esq. at the July 15, 2011 hearing. John A. DiCaro, Esq., a member of Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC, submitted an affidavit and memorandum of law opposing sanctions.
Plaintiff HSBC’s various counsel and Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC, in their opposition affidavits and memoranda of law, devote most of their opposition to my rationale for the July 1, 2011 decision and order, dismissing the instant action with prejudice and ordering a Part 130 sanctions hearing. I will not engage in debate with counsel for HSBC or Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC about my reasoning in the July 1, 2011 decision and order. As of today, neither HSBC’s counsel, whether it is Ruppe, Baase, Pfalzgraf, Cunningham, Coppola, LLC or Mayer Brown, LLP, nor Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC have moved for leave to renew or reargue my July 1, 2011 decision and order or file a notice of appeal. If HSBC’s various counsel and/or Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC dispute any part of my July 1, 2011 decision and order, why are they sitting on their hands?
Further, as indicated by the Musarra affidavit and the Michael Ware Memorandum of Law, HSBC sounds like a combination of Pontius Pilate and Sergeant Schultz in the classic 1960’s television comedy, Hogan’s Heroes. HSBC washes its hands of any responsibility and places any blame upon OCWEN, its servicer for the TAHER mortgage. To paraphrase Matthew 27:24, in the New Testament, “when HSBC saw that it could prevail nothing, but that rather a tumult was made, it took water, and washed its hands before the multitude, saying, ‘I am innocent of responsibility and should not be sanctioned.'” John Banner, the actor who played the inept Sergeant Hans Schultz, a guard in World War II’s Stalag 13, would feign ignorance about the escapades of his Allied prisoners by telling his commandant, Colonel Klink, “I know nothing! Nothing!”Moreover, Mr. Ware, in his Memorandum of Law, at page 3, states that “[t]he
administration of mortgage loans owned by the Trust is Ocwen’s responsibility under the Servicing Agreement reproduced as Musarra Ex. B” and “[g]iven the respective responsibilities of the Indenture Trustee and the Servicer, it is no suprise that the Taher loan never came to the attention of the relevant department of HSBC until after the July 1 Order became public.” Mr. Ware, concludes, at page 5, “[I]f sanctionable misconduct took place here, the Court should bear in mind that neither HSBC nor Dorner was in any practical position to control the prosecution of this action.”
July 15, 2011 Part 130 hearing for costs and sanctions
The first issue I had to address at the July 15, 2011 Part 130 hearing was determining who represented HSBC. Marco Cercone, Esq. of Ruppe, Baase, Pfalzgraf, Cunningham, Coppola, LLC answered for HSBC and satisfactorily explained to my satisfaction that OCWEN’s Assistant General Counsel substituted Ruppe, Baase, Pfalzgraf, Cunningham, Coppola, LLC for Shapiro DiCaro & Barak, LLC, pursuant to a power of attorney from HSBC to OCWEN. I then addressed Mr. Ware, and asked him how he could represent HSBC, if Mr. Cercone represented HSBC. Mr. Ware attempted to make a distinction between HSBC as an indenture trustee and in its corporate capacity. The following colloquy took place at the hearing, p. 7, line 19 – p. 10, line [*13]22:
THE COURT: Wouldn’t you have to file for intervener
status by motion?
MR. WARE: Certainly. We read the order of July 1st as making
Irene Dorner a respondent at today’s hearing.
THE COURT: . . . I ordered Ms. Dorner to appear because she’s
the President and CEO of HSBC USA, N.A. as indenture trustee.
Whatever you call it, she’s the head of HSBC. We could agree on that?
MR. WARE: Yes.
THE COURT: She’s the President and CEO of HSBC USA.
They’re the indenture trustee. That’s what the caption said. As I
said in my decision, in effect, to look at HSBC as a firm. She’s the
captain of the ship. She has to take responsibility for the good and
bad, like the manager of a baseball team. If HSBC is a baseball
team, if the team wins, you get a lot more money, a lot of aggravation.
Your team come in last, you get fired, you’re gone, you’re history,
adios. That’s what she has to bear here.
Because I have problems here with this case, and I want to get
to the bottom of what happened, I haven’t made any rulings. I didn’t
say there should be sanctions. I want to give everybody a chance to
be heard it there’s sanctionable conduct here. That’s how my order
appears. So based on that, I know Mr. Cercone represents her. Since
now her attorney-in-fact is now substituting his firm for Shapiro and
DiCaro, and you’re suddenly telling me that they don’t represent Irene
Dorner, HSBC, fascinating.
So, who represents HSBC, your or him? I don’t know. Basically,
right now he does. He just proved to me he has a power of attorney.
So the only thing I could think of, if I can split that hair and allow you
to intervene on behalf of – – what I’ll call corporate HSBC, as opposed
to indenture trustee HSBC, is that you have to file a motion on papers,
which you have not. [*14]
MR. WARE: Well, I certainly appear, your Honor, for Ms. Dorner.
THE COURT: Well, I’ll cut through the chase because I read your
papers. For argument’s sake, let’s play this out to the end. Suppose I find
that HSBC did something that requires sanctions? Dismiss as a party?
I know Ms. Dorner is the President and CEO, not an individual. I know
I can’t sanction Ms. Dorner. If that’s what the company is, it’s HSBC
that I might be able to sanction, not Ms. Dorner as an individual. I’ll
grant you that much.
Now that we’ve got Ms. Dorner protected as an individual, but
not HSBC, how are you here in the case? You didn’t file to intervene.
Unless you pull a rabbit out of your hat, in about a moment, I am going
to ask you to leave.
You’re going to stay in the room, obviously. This is a public
courtroom, but I don’t see how you can sit at the table. You’re not in
the case. HSBC, is it your firm or Mr. Cercone’s firm? If you
want to confer with him, I’ll allow you a moment to confer with him.
It’s up to you.
MR. WARE: The foreclosure is entrusted to the servicer. Ocwen
as the servicer is entitled to control the action that is now dismissed.
THE COURT: Okay.
MR. WARE: So we’re here in the aftermath of the dismissal of
the action to address the issues in the order of July 1st.
THE COURT: To use your term aftermath, in the aftermath,
doesn’t Mr. Cercone speak for HSBC since they’re the parties in the
aftermath as indenture trustee, or are you telling me he doesn’t represent
HSBC, you do? Who represents HSBC or is this going to be – – let’s
throw Ocwen under the bus because we didn’t do anything. That seems
to be the defense.
The defense is we didn’t do anything. Ocwen did it. That’s
what you’re telling me.
MR. WARE: Well, it’s certainly true, as a matter of fact, your
Honor, that – – [*15]
THE COURT: That’s what you say.
Ultimately, I allowed Mr. Ware to sit in the well next to Mr. Cercone and act as his co-counsel, but not to intervene in the case, since “corporate” HSBC did not make a motion on notice to intervene. This was done after the following exchange, at p. 11, line 9 – p. 12, line 20.
THE COURT: But here’s the problem. HSBC’s name is in the
caption. They’re the Plaintiff as indenture trustee, et cetera. So now I
find there’s a question about what occurred in this particular case in
terms of whether or not there’s something that is sanctionable.
The question is somebody has to represent HSBC. Mr. Cercone
has been substituted for Shapiro and DiCaro. He showed me the power
of attorney as I asked him to do. You magically appear.
Somebody gives these papers to me at 12:40 this afternoon, and
you say Mayer Brown, LLP is the attorney for HSBC in its corporate
capacity and not as an indenture trustee, but nowhere in the caption did
I see HSBC in its corporate capacity as a party. Therefore, you’re
attempting to intervene without making a motion.
MR. WARE: I understand you’re point, your Honor. Let me
make one point on it and then a suggestion, which is that we thought
the reading of the order of July 1st is that the bank’s assets were
imperiled by this order.
THE COURT: Imperiled. You know HSBC is a corporation.
They can afford to pay Ms. Dorner $2.3 million a year without blinking
an eyelash. What’s the worst that Judge Schack can do? Sanction them?
What’s the worst I can sanction the bank? $10,000. I don’t think it’s
going to affect the bottom line too much.
Right now . . . HSBC will not file for chapter 11 because of
whatever I do one way or the other.
MR. WARE: HSBC didn’t even get touched, your Honor.
THE COURT: I’m glad to hear that.
MR. WARE: I would be happy to be of counsel to him [Mr.
Cercone] with him as trial counsel and counsel of record for HSBC Bank.
With HSBC’s representation finally resolved, the Court inquired about HSBC’s missing President and CEO, Irene M. Dorner, who was ordered, in my July 1, 2011 decision and order, to [*16]appear for the Part 130 hearing. The following colloquy took place, at p. 15, line 1 – p. 16, line 2:
THE COURT: Now we come to why I brought everybody here.
Let me ask Mr. Cercone a question. I have obviously counsel here, Mr.
Cassara, and we have Shapiro DiCaro and Barak. You’re producing
Ms. Dorner on behalf of HSBC?
MR. CERCONE: I am not, Judge. She’s out of the country;
she’s unavailable.
THE COURT: Where out of the country?
MR. CERCONE: I do not know.
THE COURT: You don’t communicate with your client?
MR. CERCONE: I have not communicated with Ms. Dorner.
THE COURT: Maybe you can whisper in his [Mr. Ware, seated
next to Mr. Cercone] ear, and he can whisper something to you. Maybe
he knows where she is.
MR. CERCONE: She’s aware, and she appeared by counsel.
THE COURT: She’s aware. Is she away or on the lam? Where
is she? She’s not here.
MR. CERCONE: She’s not here, Judge.
THE COURT: Why is she violating the court order?
MR. CERCONE: I don’t believe she’s violating the court order,
Judge, because she’s here by counsel.
THE COURT: That’s your opinion for the moment.
Then, the Court reviewed the factual history of the case, including: the use of robosigners Christina Carter and Scott Anderson; HSBC’s lack of standing with the ineffective MERS to HSBC assignment; and, HSBC’s admission, in a prior case before me, HSBC Bank USA v Yeasmin, 24 Misc 3d 1239 (A), that HSBC doesn’t properly determine risk when buying mortgage loans in default. I then made the following statement, at p. 20, line 19 – p. 21, line 16:
Why do I have to waste my time on this? You know we have very
limited resources in our court system. You saw it today. We had to
wait to get a court officer. We probably have 25 less court officers in
this building now, approximately. I don’t know the number we had last
year at this time.
Between buy-outs, people retired, layoffs, the government and [*17]
legislative cuts, the Court’s budget, we have to cut off trials at 4:30, but
the workload increases. So we’re busy. I would like to have serious
cases that have serious issues to deal with rather than deal with these
things which are ridiculous. But I have to deal with this foreclosure.
I have to deal with what is in front of me.
That’s why I have a question of whether or not the conduct that
occurred here . . . is sanctionable, whether it be by HSBC or its attorneys.
That’s why I called for this hearing. So my first question would be with
respect to Shapiro and DiCaro, and Mr. Cassara. My question is, how
could I get an affirmation on whether everything is accurate when it’s not?
Mr. Cassara was sworn in a witness and questioned by his counsel. After his attorney asked questions, I then inquired about HSBC’s use of robosigners, Scott Anderson, Margery Rotundo and Christina Carter. The following exchange took place at p. 25, line 11 – p. 28, line 2:
THE COURT: You gave me an affirmation, as I mentioned, dated
January 6, 2011, and you say you spoke to a representative of Plaintiff.
How come you didn’t say she worked for Ocwen?
THE WITNESS: To be honest with you, Your Honor, when
the word representative of the Plaintiff – – Ocwen is their authorized
agent to handle their loan servicing , and I believed, and I still believe
that representative meant someone who represents – –
THE COURT: Don’t you think it would be helpful for the Court
when you put her name in here [the Affirmation] if it said Manager of
Account Management for Ocwen Loan Servicing as servicer or something
to that effect?
THE WITNESS: Now, yes, your Honor. Now I believe if the
Court would have inquired, I would have indicated such, to be honest
with you. At the time, and I still do believe, the word representative
meant the servicing agent or any party – –
THE COURT: Put the Court to the side for a moment. Somebody
is the reader of this affirmation. And they see the name Christina Carter
is the person you spoke to and communicated with. It says, “Manager of
Account Management.”
Wouldn’t somebody assume she’s employed by HSBC, not [*18]
another entity?
THE WITNESS: To be honest with you, your Honor, I believe
that a representative of the Plaintiff was the servicer. There was no
intent to deceive, certainly – –
THE COURT: Doesn’t it sort of fog the issue or create some
confusion that she does not work for HSBC?
THE WITNESS: Your Honor, I believe she was a representative
of the Plaintiff, that’s sincere.
THE COURT: Then you say everything is accurate. . . the assignor
has the same address as the assignee.
That’s a little bizarre, or try it another way. Scott Anderson, how
does he become both the assignor and the assignee?
THE WITNESS: I’m sorry, your Honor – –
THE COURT: Scott Anderson is the alleged Vice President of
MERS. Are you aware that he is employed by Ocwen?
THE WITNESS: Yes.
THE COURT: And he’s the assignor. Who is the assignee of
Ocwen? Isn’t he conflicted?
THE WITNESS: I’m not following.
THE COURT: Scott Anderson is not conflicted?
THE WITNESS: Your Honor, I believe – –
THE COURT: You believe he is?
THE WITNESS: I don’t know the answer.
THE COURT: Better speak up. That’s one question. Margery
Rotundo signed the affidavit of merit. You’re aware of the fact that
she wears three or four different corporate hats in cases before me?
THE WITNESS: I was not aware or do not recall it was.
THE COURT: And then you’ve got Christina Carter who wears
many hats. This woman you spoke to, are you aware of that also?
THE WITNESS: I was not aware of that as well.
THE COURT: So you’re not aware of that?
THE WITNESS: Okay. [*19]
After further attempts by counsel for HSBC and Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC to argue about the rationale for my July 1, 2011 decision and order, I concluded the hearing and reserved decision.
Frivolous conduct and 22 NYCRR § 130-1.1
22 NYCRR § 130-1.1 (a) allows the Court, in its discretion, to “impose financial
sanctions upon any party or attorney in a civil action or proceeding who engages in frivolous conduct as defined in this Part, which shall be payable as provided in section 130-1.3 of this Part.” 22 NYCRR § 130-1.1 (c) states that:
conduct is frivolous if: (1) it is completely without merit in law and cannot be supported by a reasonable argument for an extension, modification or reversal of existing law;
(2) it is undertaken primarily to delay or prolong the resolution of the litigation, or to harass or maliciously injure another; or
(3) it asserts material factual statements that are false.
Conduct is frivolous and can be sanctioned under the above court rule if “it is completely without merit . . . and cannot be supported by a reasonable argument for an extension, modification or reversal of existing law.” (Gordon v Marrone, 202 AD2d 104, 110 [2d Dept 1994] lv denied 84 NY2d 813 [1995]). (See RKO Properties v Boymelgreen, 77 AD3d 721 [2d Dept 2010]; Finkelman v SBRE, LLC, 71 AD3d 1081 [2d Dept 2010]; Glenn v Annunziata, 53 AD3d 565 [2d Dept July 15, 2008]; Miller v Dugan, 27 AD3d 429 [2d Dept 2006]; Greene v Doral Conference Center Associates, 18 AD3d 429 [2d Dept 2005]; Ofman v Campos, 12 AD3d 581 [2d Dept 2006]).
In determining if sanctions are appropriate, the Court must look at the broad pattern of conduct by the offending attorneys or parties. (Levy v Carol Management Corporation, 260 AD2d 27 [1d Dept 1999]). The Levy Court, at 33, held that, “22
NYCRR 130-1.1 allows us to exercise our discretion to impose costs and sanctions on an errant party under circumstances particularly applicable here. The relief may include, inter alia, sanctions against the offending party or its attorney (22 NYCRR 130-1.1 [1]) in an amount to be determined by us, which we would make payable to the Lawyers’ Fund for Client Protection (22 NYCRR 130-1.3)” Further, the Levy Court instructed, at 34, that “[s]anctions are retributive, in that they punish past conduct. They also are goal oriented, in that they are useful in deterring future frivolous conduct not only by the particular parties, but also by the Bar at large.” The Court, in Kernisan, M.D. v Taylor (171 AD2d 869 [2d Dept 1991]), noted that the intent of the Part 130 Rules “is to prevent the waste of judicial resources and to deter vexatious litigation and dilatory or malicious litigation tactics (cf. Minister, Elders & Deacons of Refm. Prot. Church of City of New York v 198 Broadway, 76 NY2d 411; see Steiner v Bonhamer, 146 Misc 2d 10) [Emphasis added].”
Clearly, the pattern of conduct in the instant action by plaintiff HSBC is subject to sanctions. [*20]HSBC’s use of robsigners is “completely without merit in law or fact.” In my July 1, 2011 decision and order I documented the conflicted conduct of robosigners Scott Anderson, Margery Rotundo and Christina Carter and signature variations used by Scott Anderson and Christina Carter. Further, the attempt of “corporate” HSBC to intervene on July 15, 2011 without making a motion on notice is “without merit in law” and “a waste of judicial resources.”
While the Court cannot sanction HSBC’s President and CEO Irene Dorner, since she appeared by counsel, her conduct by failing to appear at the July 15, 2011 hearing without any reasonable explanation is without merit. As the leader of HSBC she could have shed some light on what happened in this action. She was missing in action, demonstrating her personal contempt for the Supreme Court of the State of New York. Mr. Cercone, her counsel, stated she was out of the country, but aware of the Court hearing. However, he stated “I have not communicated with Ms. Dorner.” Therefore, how did he know she was aware of the hearing or even out of country?
Moreover, HSBC’s Pontius Pilate/Sergeant Schultz defense is absurd. The case caption states that HSBC is the plaintiff, not OCWEN. If HSBC has its name on the caption, it can’t claim ignorance. HSBC as plaintiff is responsible for the actions of its agents, such as OCWEN. Mr. Ware’s claim that “neither HSBC not Dorner was in any practical position to control the prosecution of this action” is ludicrous. This does not absolve HSBC of its corporate sins. If HSBC is a ship, Ms. Dorner is the Captain and responsible for both the good and the bad. However, in the instant action, HSBC appears to be the RMS Titanic. Ms. Dorner, unlike Captain Edward Smith of the RMS Titanic, did not go down with the ship after it struck an iceberg.
Further, plaintiff HSBC and its counsel, Shapiro DiCaro & Barak, LLC, engaged in frivolous conduct by asserting false material representations, including claims that HSBC: owned the TAHER note; had standing to prosecute the instant action; and, had offices at 1661 Worthington Road, Suite 100, West Palm Beach, FL 33409 [OCWEN’s offices]. Further, in Mr. Cassara’s January 6, 2011 affirmation “under the penalties of perjury” he asserted that an OCWEN employee, robosigner Christiana Carter, was a representative of HSBC and that the best of Mr. Cassara’s “knowledge, information, and
belief, the Summons and Complaint, and other papers filed or submitted to the Court in this matter contain no false statements of fact or law.” “Nothing could more aptly be described as conduct completely without merit in fact’ than the giving of sworn testimony or providing an affidavit, knowing the same to be false, on a material issue.” (Sanders v Copley, 194 AD2d 85, 88 [1d Dept 1993]). Conduct of counsel is “frivolous because it was without merit in law and involved the assertion of misleading factual statements.” (Curcio v J.P. Hogan Coring & Sawing Corp., 303 AD2d 357, 358 [2d Dept 2003]).
In Navin v Mosquera (30 AD3d 883 [3d Dept 2006]), the Court instructed that when considering if specific conduct is sanctionable as frivolous, “courts are required to
examine whether or not the conduct was continued when its lack of legal or factual basis was apparent [or] should have been apparent’ (22 NYCRR 130-1.1 [c]).” In Sakow ex rel. Columbia Bagel, Inc. v Columbia Bagel, Inc. (6 Misc 3d 939, 943 [Sup Ct, New York County 2004]), the Court held that “[i]n assessing whether to award sanctions, the Court must consider whether the attorney adhered to the standards of a reasonable attorney (Principe v Assay Partners, 154 Misc [*21]2d 702 [Sup Ct, NY County 1992]).” In the instant action, a reasonable attorney would not have affirmed under penalties of perjury that Christina Cater was a representative of HSBC, but would explain that she was an employee of its servicer, OCWEN. Therefore, the course of conduct of Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC, and Frank Cassara, Esq., in the instant action, was not reasonable.
In this time of budgetary constraints, when our Courts have an increased caseload but less funding, the Court cannot countenance the continuation of actions which waste scarce judicial resources. Therefore, based upon the totality of frivolous conduct in this matter by plaintiff HSBC and its counsel, Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC, the Court finds it is appropriate to impose sanctions of $10,000.00 upon plaintiff HSBC and $5,000.00 upon Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC.
Conclusion
Accordingly, it is
ORDERED that, after conducting a hearing on July 15, 2011, to determine if plaintiff HSBC BANK USA, N.A., AS INDENTURE TRUSTEE FOR THE REGISTERED NOTEHOLDERS OF RENAISSANCE HOME EQUITY LOAN TRUST 2007-2, plaintiff’s counsel Frank M. Cassara, Esq. and his firm Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC engaged in “frivolous conduct,” as defined in the Rules of the Chief Administrator, 22 NYCRR § 130-1 (c) and that plaintiff HSBC BANK USA, N.A., AS INDENTURE TRUSTEE FOR THE REGISTERED NOTEHOLDERS OF RENAISSANCE HOME EQUITY LOAN TRUST 2007-2, plaintiff’s counsel Frank M. Cassara, Esq. and his firm Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC were granted “a reasonable opportunity to be heard,” pursuant to the Rules of the Chief Administrator, 22 NYCRR § 130-1.1 (d), the Court finds that plaintiff HSBC BANK USA, N.A., AS INDENTURE TRUSTEE FOR THE REGISTERED NOTEHOLDERS OF RENAISSANCE HOME EQUITY LOAN TRUST 2007-2 and the law firm of Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC engaged in “frivolous conduct,” as defined in 22 NYCRR § 130-1.1, in the instant matter; and it is further
ORDERED that plaintiff HSBC BANK USA, N.A., AS INDENTURE TRUSTEE FOR THE REGISTERED NOTEHOLDERS OF RENAISSANCE HOME EQUITY LOAN TRUST 2007-2, pursuant to the Rules of the Chief Administrator, 22 NYCRR
§ 130-1.3, shall pay a sanction of $10,000.00, to the Lawyer’s Fund for Client Protection, 119 Washington Avenue, Albany, NY 12210, within thirty (30) days after service of this decision and order; and it is further
ORDERED that the law firm of Shapiro, DiCaro & Barak, LLC, pursuant to the Rules of the Chief Administrator, 22 NYCRR § 130-1.3, shall pay a sanction of $5,000.00, to the Lawyer’s Fund for Client Protection, 119 Washington Avenue, Albany, NY 12210, within thirty (30) days after service of this decision and order; and it is further
ORDERED, that Ronald David Bratt, Esq., my Principal Law Clerk, is directed to serve this order by first-class mail, upon: Irene M. Dorner, President and Chief Executive Officer of plaintiff, HSBC BANK USA, N.A., AS INDENTURE TRUSTEE FOR THE REGISTERED NOTEHOLDERS OF RENAISSANCE HOME EQUITY LOAN TRUST 2007-2, 452 Fifth Avenue, New York, New York 10018; and, Shapiro DiCaro & Barak, LLC, 250 Mile Crossing Boulevard, Suite One, Rochester, New York 14624. [*22]
This constitutes the Decision and Order of the Court.
ENTER
___________________________
Hon. Arthur M. SchackJ. S. C
[ipaper docId=76394426 access_key=key-1tpxiizxns7vihs5nlvi height=600 width=600 /]
© 2010-19 FORECLOSURE FRAUD | by DinSFLA. All rights reserved.



























Recent Comments